Configuration management for store settings
Configuration management, or Pipeline Deployment, provides a way to deploy across your environments with minimal downtime. The process extracts all configuration settings from your Magento implementation into a single file. Add this file to your commit and push it across all of your environments to keep consistent settings and reduce downtime. It provides the following benefits:
- Better way to manage and synchronize the configuration across your Integration, Staging, and Production environments.
- Less time required to build and deploy your project by moving static file deployment from deploy to the build phase. Your site is in maintenance mode until deployment completes. For details, see Deployment Process.
- Sensitive data is automatically added into an environment variables file (
/app/etc/env.php). You can also manually add sensitive environment variables using the Project Web Interface, the CLI, or directly in the Magento Admin. For example, payment processor passwords and API keys.
These methods are optional, but strongly recommended. The process ensures faster deployments and consistent configurations across your environments.
To complete configuration management tasks, you must have a project reader role with environment administrator privileges.
For extended technical information, see Pipeline Deployment. When configuring and using these features, follow this topic specifically. Magento Commerce Cloud provides the build server, build and deploy scripts, and deployment environments. You only need to configure settings, generate the file, and deploy.
How it works
The database contains default configurations for your Magento store. When you update the configurations in the Integration, Staging, and Production environments using the Magento Admin, you generate a file of all Magento configuration settings into a single text file: app/etc/config.php.
To generate the file, use one of the following:
php vendor/bin/m2-ece-scd-dump—Recommended Exports only modified configuration settingsphp ./vendor/bin/ece-tools config:dump—Exports every configuration setting, including modified and default settings
For Magento Commerce Cloud, we do not recommend using the app:config:dump command. This command pulls and locks all values in a read-only state. This affects Fastly and other important modules.
Any data that exports to the file becomes locked. The corresponding field in the Magento Admin becomes read-only. This ensures consistent configurations as you push the file across all environments. And every time you run this command, any new configurations are appended to your config.php file. If you need to modify or delete an existing configuration, you must edit the file manually.
By using the scd-dump command, you can configure only the settings you want copied across all environments. After you merge the code, you can configure additional settings in Staging and Production. For sensitive configurations, you can also add those settings to environment variables. For example, you may want to add different PayPal merchant account credentials for Staging (sandbox) and Production (live).
If sensitive data is found in your configurations, it is generated as environment variables to env.php. This file remains in the environment and should not be added to your Git environment.
Switching between commands
Can you switch between using php vendor/bin/m2-ece-scd-dump and php ./vendor/bin/ece-tools config:dump? Only in one specific way.
In 2.2 and later, you cannot delete the config.php file to regenerate it. You can only edit the file to change or remove a value. This file includes more information than just configuration values.
If you use php vendor/bin/m2-ece-scd-dump to generate the file, you can switch to php ./vendor/bin/ece-tools config:dump. Once switched, you cannot switch back. Using the command will append the file with all configured values (default and modified) not currently captured in the file. Any modified values must be entered by editing the file.
Configuration data
System settings refer to the configurations in the Magento Admin in Stores > Settings > Configuration. Depending on the command used, all or just modified system configurations save to the file.
This file can include all system configuration settings for stores, sites, extensions, and static file optimization settings. System values related to static content deployment (for example, static file optimization) are also stored in app/etc/config.php. Static file optimization means merging and minifying JavaScript and Cascading Style Sheets, and minifying HTML templates.
Sensitive values are not stored in app/etc/config.php. Any sensitive configurations should export to app/etc/config.php during the scd-dump process. You can also create environment variables using CLI commands or the Project Web Interface.
You can set any value using environment variables, but we recommend using environment variables for sensitive values.
For a list of configurable settings, see Configuration settings you can change and System settings reference.
Static content deployment performance
Depending on the size of your store, you may have a large amount of static content files to deploy. Normally, static content deploys during the deploy phase, which is in Maintenance mode. To move the deployment of static content to the build phase, generate the configuration file.
If you generate a config.php file, the build and deploy hooks identify the file and deploy all static files during the build phase. This helps reduce the time spent in Maintenance mode during the deploy phase.
Before deploying static files, the build and deploy phases compress static content using gzip. Compressing static files reduces server loads and increases site performance. Refer to Magento build options to learn about customizing or disabling file compression.
Configuration selection flow
All system configurations are set during deployment according to the following override scheme:
- If an environment variable exists, use the custom configuration and ignore the default configuration.
- If an environment variable does not exist, use the configuration from a
MAGENTO_CLOUD_RELATIONSHIPSname-value pair in the.magento.app.yamlfile. Ignore the default configuration. - If an environment variable does not exist and
MAGENTO_CLOUD_RELATIONSHIPSdoes not contain a name-value pair, remove all customized configuration and use the values from the default configuration.
Configuration settings you can change
The following table shows the configuration settings affected by the php vendor/bin/m2-ece-scd-dump command. These are the configuration settings that you can manage in Git. If you use php ./vendor/bin/ece-tools config:dump, all settings are exported including default and modified settings.
The config.php file includes the following settings and configuration values:
- Configured values for settings entered through the Magento Admin (see the table below)
- Configured extension settings
- Scopes value for static content deployment (default is
quick)
| Description | Path in Magento Admin: Stores > Settings > Configuration > ... |
|---|---|
| Store locale | General > General, Locale Options > Locale |
| Static asset signing | Advanced > Developer, Static Files Settings > Static Files Signing |
| Server-side or client-side LESS compilation | Advanced > Developer, Frontend Developer Workflow > Workflow type |
| HTML minification | Advanced > Developer, Template Settings > Minify Html |
| JavaScript minification | Advanced > Developer, JavaScript Settings > (several options) |
| CSS minification | Advanced > Developer, CSS Settings > Merge CSS Files and Minify CSS Files |
| Disable modules output | Advanced > Advanced > Disable Modules Output |
Recommended procedure to manage your settings
Managing store configuration is a complex task mostly up to you. What locales do you want to use? What custom themes do you need? Instead of making these changes in every environment, you can use the config.php file, which contains a number of configuration properties that you can adjust as needed.
We strongly recommend using the scd-dump command to generate a config.php file. This file includes only the settings you configure without locking the default values. It also ensures that all extensions used in the Staging and Production environments do not break due to read-only configurations, especially Fastly.
To fully understand the process, see our extensive example.
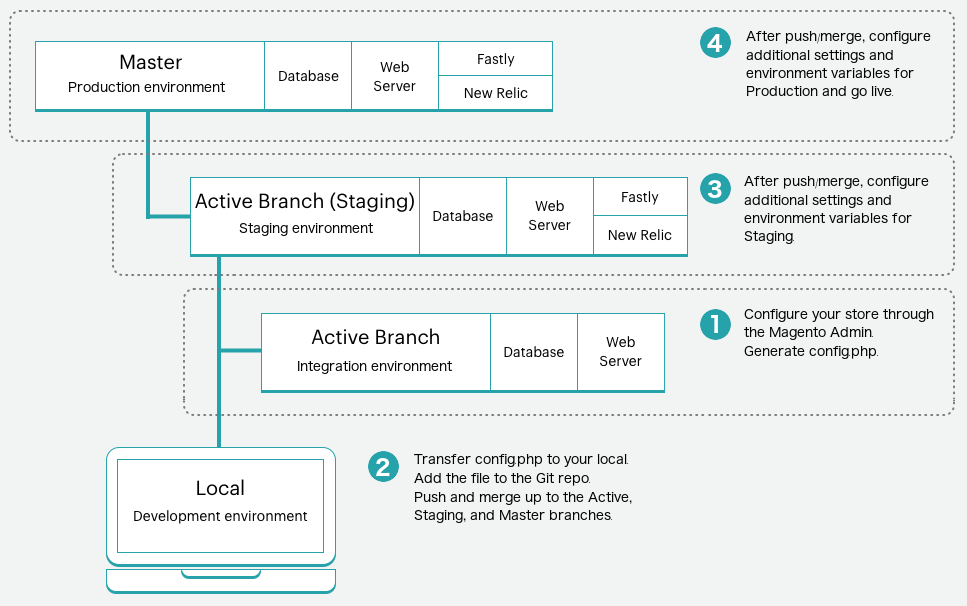
The Starter plan environment high-level overview of this process:
The Pro plan environment high-level overview of this process:
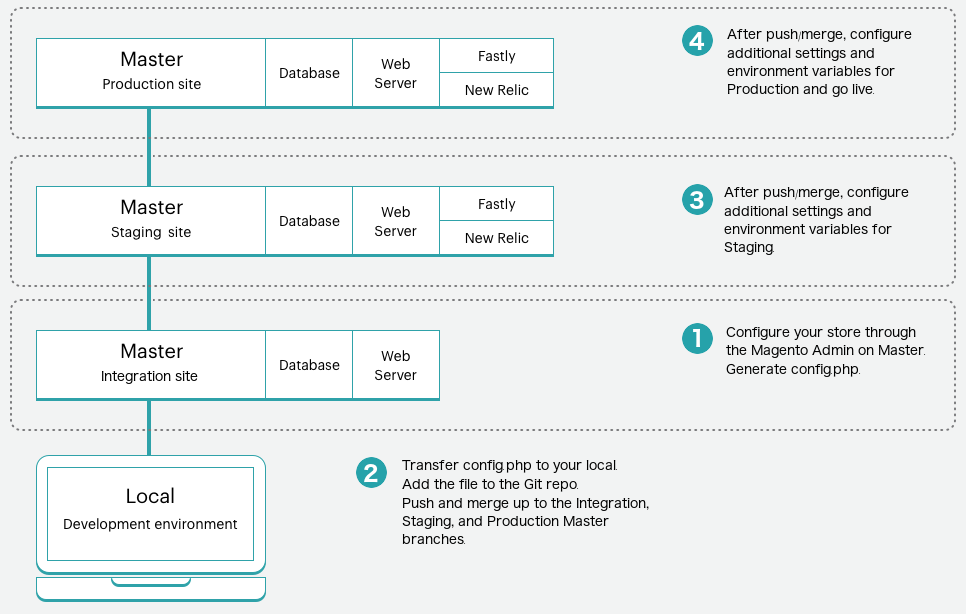
Step 1: Configure your store
Complete all configurations for your stores in the Admin console:
-
Log in to the Magento Admin for one of the environments:
- Starter: An active development branch
- Pro: Integration environment
- Create and configure all store settings. These configurations do not include the actual products unless you plan on dumping the database from this environment to Staging and Production. Typically development databases do not include your full store data.
-
Open a terminal on your local and generate
/app/etc/config.phpon the environment:1
ssh <SSH URL> "php vendor/bin/m2-ece-scd-dump"
Step 2: Transfer and add the file to Git
Push the config.php file to Git. To push this file to the master Git branch, you need to complete a few extra steps because this environment is read-only.
-
Transfer the
config.phpfile to your local system usingrsyncorscp. You can only add this file to the Git branch through your local.1
rsync <SSH URL>:app/etc/config.php ./app/etc/config.php
-
Add and push the
config.phpfile to the Git master branch.1
git add app/etc/config.php && git commit -m "Add system-specific configuration" && git push origin master
When you add the config.php file to Git, all build and deploy processes move static content deployment (SCD) to the build phase. The method for the deployment uses the scope. The default option is quick. You can change the strategy by setting an environment variable for SCD_STRATEGY.
Once you add this file to your code, you should not delete it. If you need to remove or edit settings, you must manually edit the file to make changes.
Step 3 & 4: Push Git branch to Staging and Production
Log in to the Magento Admin panel in those environments to verify the settings. Only configured settings display when you use the scd-dump command. Continue configuring the environment, if needed.
For Starter, when you push, the updated code pushes to the active environment. Merge the branch to Staging and Production. Complete any additional configurations in Staging and Production as needed.
For Pro, when you push to the Git branch, the Integration master environment updates. Deploy this branch to Staging and Production. Complete any additional configurations in Staging and Production as needed.
Update configurations
If you need to modify or remove any existing configuration settings in the config.php file, you will need to modify the file manually with a text editor. After completing edits or removals, you can push it to Git to update.
To add new configurations, modify your environment through the Magento Admin panel and run the command again to generate the file. Any new configurations are appended to the code in the file. Push it to Git to update.
While you can manually edit the config.php file in the Staging and Production environments, we do not recommend it. The file helps to keep all configurations consistent across all environments. Never delete the config.php file to rebuild it. Deleting the file can remove specific configurations and settings required for build and deploy processes.
Migrate configurations
If you upgrade to Magento Commerce Cloud 2.2 or later, you may want to migrate settings from the config.local.php file to your new config.php file. If the configuration settings in your Magento Admin panel match the contents of the file, follow the instructions to generate and add the config.php file.
If they differ, you can append content from the config.local.php file to your new config.php file:
- Follow instructions to generate the
config.phpfile using the recommended method. - Open the
config.phpfile and delete the last line. - Open the
config.local.phpfile and copy the contents. - Paste the contents into the
config.phpfile, save, and complete adding it to Git. - Deploy across your environments.
You only need to complete this migration once. When you need to update the file, always update the config.php file.
Change locales
You can change your store locales without following a complex configuration import and export process, if you have SCD_ON_DEMAND enabled. You can update the locales using the Admin panel.
You can add another locale to the Staging or Production environment by enabling SCD_ON_DEMAND in an Integration branch, generate an updated config.php file with the new locale information, and copy the configuration file to the target environment.
This process overwrites the store configuration; only do the following if the environments contain the same stores.
- From your Integration environment, enable the
SCD_ON_DEMANDvariable. - Add the necessary locales using your Admin panel.
-
Generate the
app/etc/config.phpfile containing all locales.1
php ./vendor/bin/ece-tools config:dump
-
Copy the new configuration file from your Integration environment to your local Staging environment directory.
1
rsync <SSH URL>:app/etc/config.php ./app/etc/config.php
- Push code changes to the remote.
While you can manually edit the config.php file in the Staging and Production environments, we do not recommend it. The file helps to keep all configurations consistent across all environments. Never delete the config.php file to rebuild it. Deleting the file can remove specific configurations and settings required for build and deploy processes.