Indexing overview
Indexing is how Magento transforms data such as products and categories, to improve the performance of your storefront. As data changes, the transformed data must be updated or reindexed. Magento has a very sophisticated architecture that stores lots of merchant data (including catalog data, prices, users, and stores) in many database tables. To optimize storefront performance, Magento accumulates data into special tables using indexers.
For example, if you change the price of an item from $4.99 to $3.99. Magento must reindex the price change to display it on your storefront.
Without indexing, Magento would have to calculate the price of every product on the fly, taking into account shopping cart price rules, bundle pricing, discounts, tier pricing, etc. Loading the price for a product would take a long time, possibly resulting in cart abandonment.
Indexing terminology
- Dictionary
- Original data entered to the system. Dictionaries are organized in normal form to facilitate maintenance (updating the data).
- Index
- Representation of the original data for optimized reading and searching. Indexes can contain results of aggregations and various calculations. Index data can be always re-created from a dictionary using a certain algorithm.
- Indexer
- Object that creates an index.
Create custom indexers
Magento contains several indexers out of the box, but you might want to add your own if your customization requires data searches, which are not optimized by the Magento default indexers.
This topic provides a high level description of how indexing is implemented from a developer’s point of view, and practical advice for how to add your own indexer.
How Magento implements indexing
The following components are involved in the indexing process:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Magento_Indexer | Implements:
|
| Magento\Framework\Mview |
|
Magento_Indexer replaces the Magento 1.x Magento_Index module. Use Magento_Indexer for all new development.
Indexing types
Each index can perform the following types of reindex operations:
-
Full reindex, which means rebuilding all the indexing-related database tables
Full reindexing can be caused by a variety of things, including creating a new web store or new customer group.
You can optionally fully reindex at any time using the command line.
-
Partial reindex, which means rebuilding the database tables only for the things that changed (like changing a single product attribute or price)
The type of reindex performed in each particular case depends on the type of changes made in the dictionary or in the system. This dependency is specific for each indexer.
The following figure shows the logic for partial reindexing.
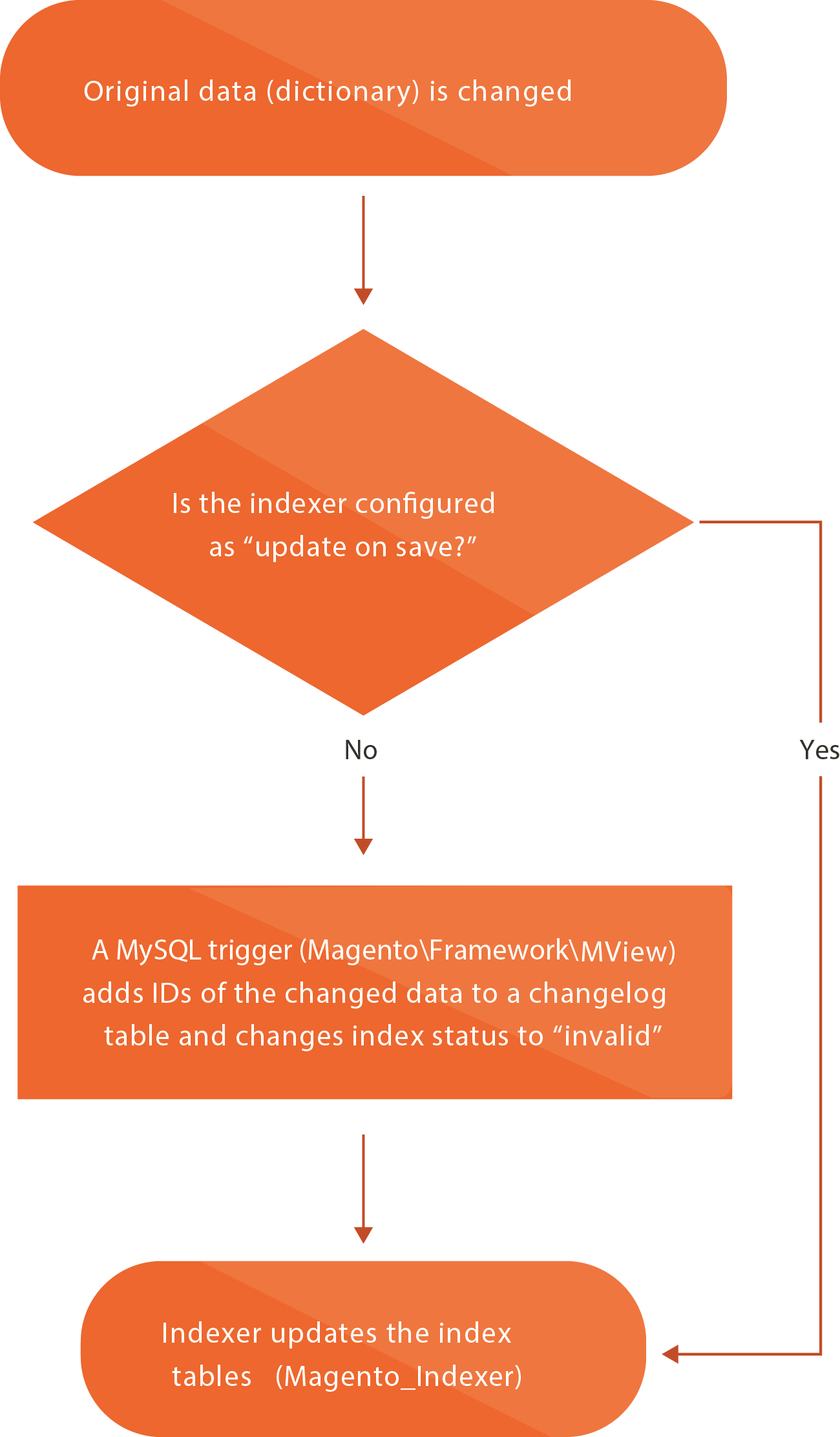
Indexer status
Depending on whether an index data is up to date, an indexer status value is one of the following:
- valid - data is synchronized, no reindex required
- invalid - the original data was changed, the index should be updated
- working - indexing is in progress
The Magento indexing mechanism uses the status value in reindex triggering process. You can check the status of an indexer in the Admin panel in System > Tools > Index Management or manually using the command line.
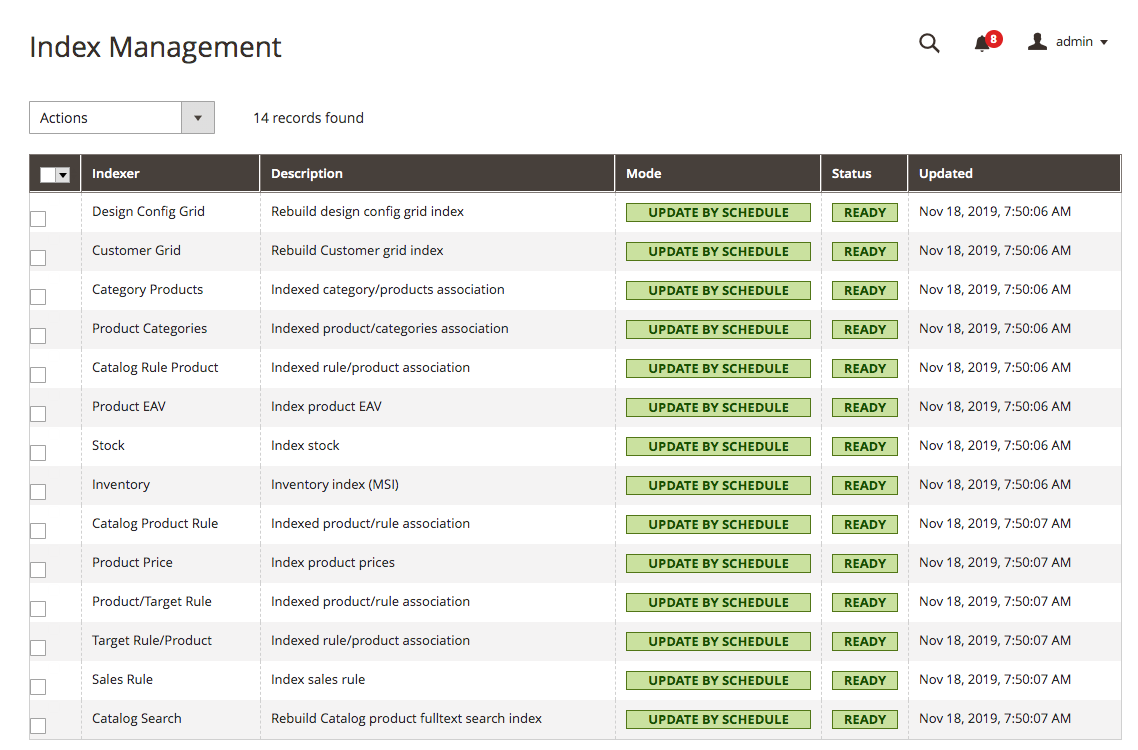
Indexing modes
Reindexing can be performed in two modes:
- Update on Save - index tables are updated immediately after the dictionary data is changed.
- Update by Schedule - index tables are updated by cron job according to the configured schedule.
Update by Schedule does not support the customer_grid indexer. You must either use Update on Save or reindex the customer grid manually (bin/magento indexer:reindex customer_grid). See the Help Center article.
To set these options:
- Log in to the Magento Admin.
- Click System > Tools > Index Management.
- Select the checkbox next to each type of indexer to change.
- From the Actions list, click the indexing mode.
- Click Submit.
You can also reindex from the command line
The following figure shows an example of setting indexers to Update by Schedule:
Mview
The mview.xml file is used to track database changes for a certain entity.
For example part of Magento/Catalog/etc/mview.xml is tracking category to product relation described in the following record:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
<!-- ... -->
<view id="catalog_category_product" class="Magento\Catalog\Model\Indexer\Category\Product" group="indexer">
<subscriptions>
<table name="catalog_category_entity" entity_column="entity_id" />
<table name="catalog_category_entity_int" entity_column="entity_id" />
</subscriptions>
</view>
<!-- ... -->
Explanation of nodes:
- The
viewnode defines an indexer. Theidattribute is a name of the indexer table, theclassattribute is indexer executor, thegroupattribute defines the indexer group. - The
subscriptionsnode is a list of tables for tracking changes. - The
tablenode defines the certain table to observe and track changes. The attributenameis a name of an observable table, the attributeentity_columnis an identifier column of entity to be re-indexed. So, in case ofcatalog_category_product, whenever one or more categories is saved, updated or deleted incatalog_category_entitytheexecutemethod ofMagento\Catalog\Model\Indexer\Category\Productwill be called with argumentidscontaining ids of entities from column defined underentity_columnattribute. If indexer type is set to “Update on Save” the method is called right away after the operation. If it set to “Update by Schedule” the mechanism creates a record in the change log table using MYSQL triggers.
A change log table is created according to the naming rule - INDEXER_TABLE_NAME + ‘_cl’, in case of catalog_category_product it will be catalog_category_product_cl.
The table contains the version_id auto-increment column and entity_id column that contains identifiers of entities to be re-indexed.
For each table node the framework automatically creates MYSQL AFTER triggers for each possible event (INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE).
For the table catalog_category_entity triggers will be created with the following statements.
INSERT operation:
BEGIN
INSERT IGNORE INTO `catalog_category_product_cl` (`entity_id`) VALUES (NEW.`entity_id`);
END
UPDATE operation:
BEGIN
IF (NEW.`entity_id` <=> OLD.`entity_id`
OR NEW.`attribute_set_id` <=> OLD.`attribute_set_id`
OR NEW.`parent_id` <=> OLD.`parent_id`
OR NEW.`created_at` <=> OLD.`created_at`
OR NEW.`path` <=> OLD.`path`
OR NEW.`position` <=> OLD.`position`
OR NEW.`level` <=> OLD.`level`
OR NEW.`children_count` <=> OLD.`children_count`)
THEN INSERT IGNORE INTO `catalog_category_product_cl` (`entity_id`) VALUES (NEW.`entity_id`);
END IF;
END
DELETE operation:
BEGIN
INSERT IGNORE INTO `catalog_category_product_cl` (`entity_id`) VALUES (OLD.`entity_id`);
END
The method Magento\Framework\Mview\ViewInterface::update is responsible for handling records in the changelog. The method is being called by CRON and
it defines IDs to be re-indexed from the change log by last applied version_id and calls the execute method for each particular indexer with IDs as an argument.
How to reindex
You can reindex by:
- Using a cron job, which is preferred because indexing runs every minute.
- Using the
magento indexer:reindex [indexer]command, which reindexes selected indexers, or all indexers, one time only.
Magento indexers
The Magento Open Source application implements the following indexers (use bin/magento indexer:info to list the indexers):
| Indexer name | Indexer method name | Indexer class | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Design Config Grid | design_config_grid |
Magento\Theme\Model\Indexer\Design\Config | |
| Customer Grid | customer_grid |
Magento\Framework\Indexer\Action\Entity | Rebuilds the customer grid index. Not supported by the Update by Schedule indexing mode. See the Help Center article. |
| Category products | catalog_category_product |
Magento\Catalog\Model\Indexer\Category\Product | Creates category/products association |
| Product categories | catalog_product_category |
Magento\Catalog\Model\Indexer\Product\Category | Creates category/products association |
| Product price | catalog_product_price |
Magento\Catalog\Model\Indexer\Product\Price | Pre-calculates product prices |
| Product entity attribute value | catalog_product_attribute |
Magento\Catalog\Model\Indexer\Product\Eav | Reorganizes the EAV product structure to flat structure |
| Stock | cataloginventory_stock |
Magento\CatalogInventory\Model\Indexer\Stock | |
| Catalog rule product | catalogrule_rule |
Magento\CatalogRule\Model\Indexer\Rule\RuleProductIndexer | |
| Catalog product rule | catalogrule_product |
Magento\CatalogRule\Model\Indexer\Product\ProductRuleIndexer | |
| Catalog search | catalogsearch_fulltext |
Magento\CatalogSearch\Model\Indexer\Fulltext |
Magento Commerce Edition contains all indexers of Magento Open Source Edition and the following ones:
| Indexer name | Indexer method name | Indexer class | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inventory | inventory |
Magento\InventoryIndexer\Indexer\InventoryIndexer |
Inventory index (MSI) |
| Product/Target Rule | targetrule_product_rule |
Magento\TargetRule\Model\Indexer\TargetRule\Product\Rule |
Indexes product/rule association |
| Target Rule/Product | targetrule_rule_product |
Magento\TargetRule\Model\Indexer\TargetRule\Rule\Product |
Indexes rule/product association |
| Sales Rule | salesrule_rule |
Magento\AdvancedSalesRule\Model\Indexer\SalesRule |
Indexes sales rule |