Web API technical vision
Web API is crucial for Magento because of the need to integrate with order management, customer management, and other enterprise management software systems.
There are many headless Magento installations in which a merchant partially uses Magento functionality, while the other pieces of an eCommerce website are provided by other systems.
See more details about the importance of web APIs in modern web applications.
Components Dependencies
The following diagram shows Web API component dependencies.
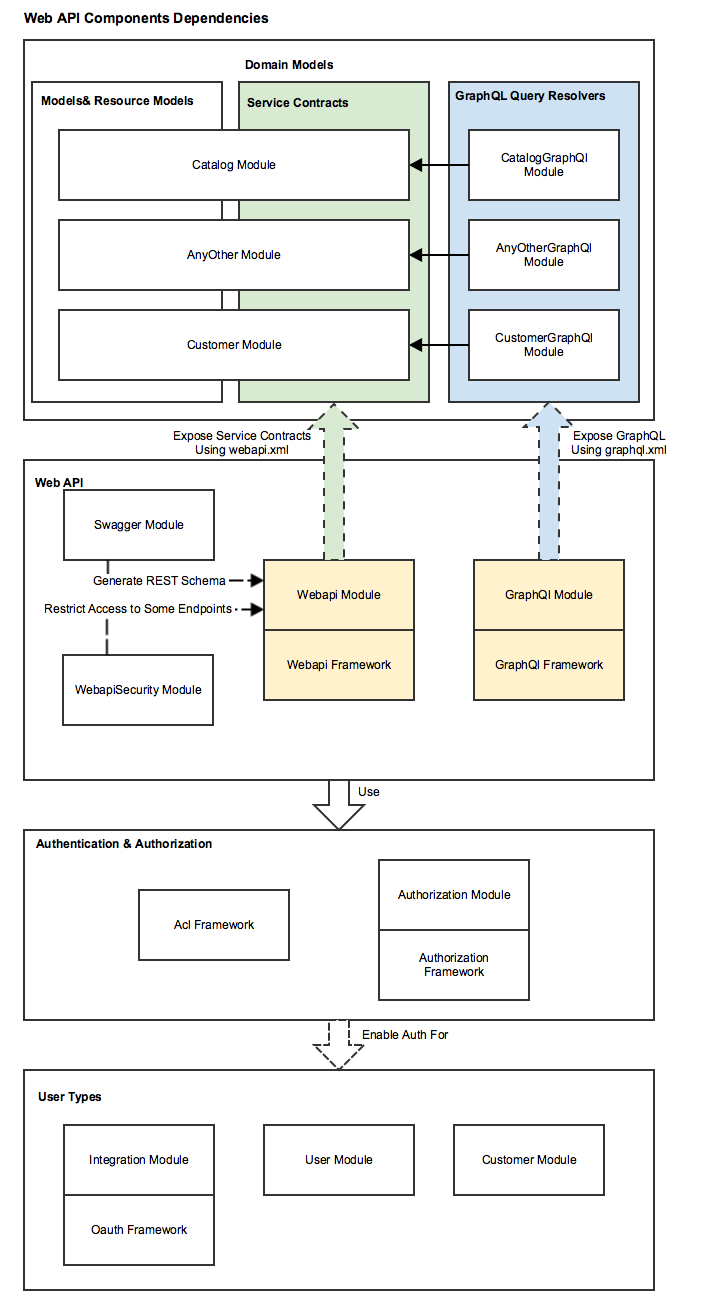
High-level Architecture
The following image provides an overview of how Web API requests are processed.
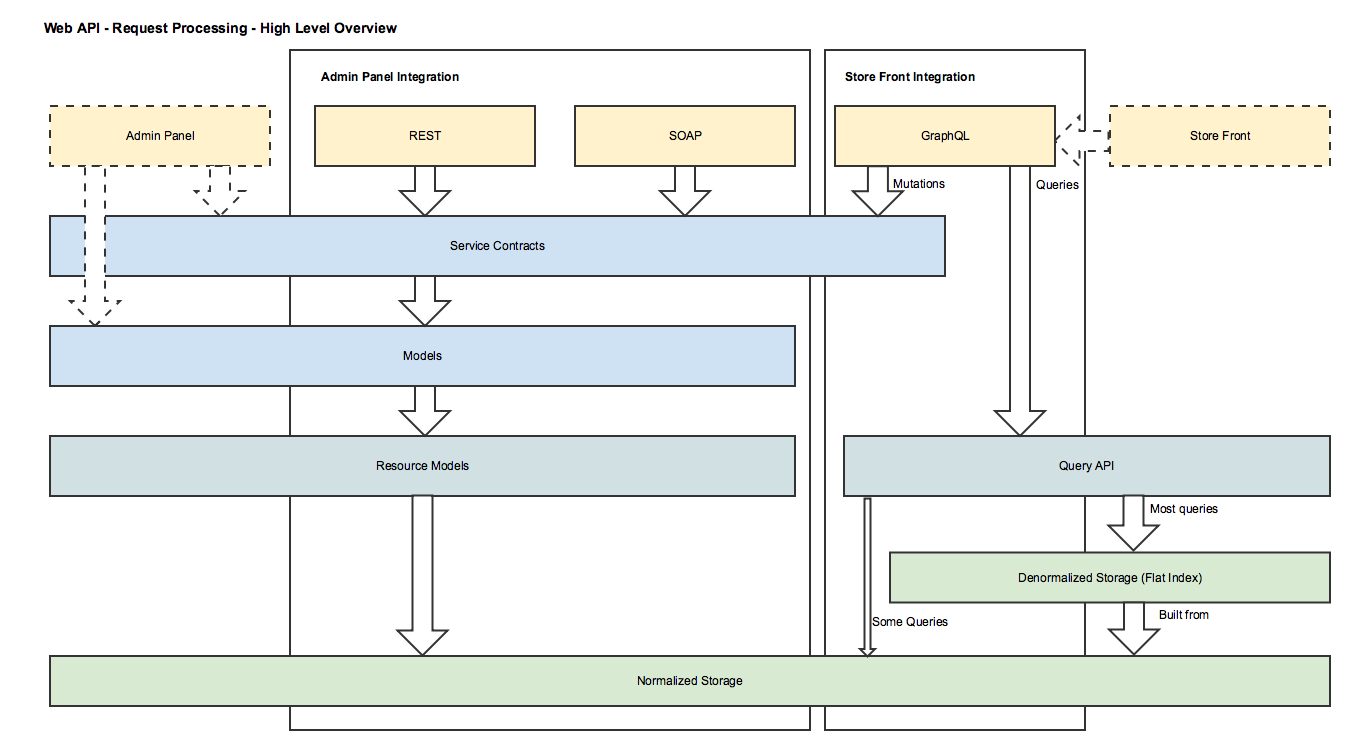
Extension Scenarios
Declare a new REST and SOAP endpoint
Any service contract can be exposed as REST and SOAP endpoints via configuration in a module’s webapi.xml file.
Declare a new GraphQL query/mutation
- Create custom resolvers.
- Declare a custom query/mutation and all necessary types in
schema.graphqls.
If the target module is called MyModule, then create the resolvers and configuration files in a new module called MyModuleGraphQl.
See the GraphQL documentation for more information.
Add a custom authentication mechanism
- Provide a custom implementation of
\Magento\Authorization\Model\UserContextInterface, that verifies a user’s identity using a custom authentication mechanism. - Declare custom user context in the composite user context for the target area(s) (
webapi_rest,webapi_soap,webapi_graphql) :
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
<type name="Magento\Authorization\Model\CompositeUserContext">
<arguments>
<argument name="userContexts" xsi:type="array">
<item name="customUserContext" xsi:type="array">
<item name="type" xsi:type="object">Vendor\Module\Model\Authentication\CustomUserContext</item>
<item name="sortOrder" xsi:type="string">100</item>
</item>
</argument>
</arguments>
</type>
Modify the schema of an existing SOAP and REST endpoint
The recommended approach for modifying an interface is to define a new endpoint. If you simply modify the schema, you might break existing integrations or extensions.
To extend an interface, use extension attributes.
Modify the schema of an existing GraphQL query
-
Add a
schema.graphqlsfile to the<ModuleName>GraphQlmodule. Magento merges this file with configurations from other modules using the same merge rules as other types of configuration. -
Write any necessary plugins for existing resolvers related to the query, or create a custom resolver and enable it via override in
schema.graphqls
Model Consistency Constraints
Any new design related to Web API must satisfy the following constraints to keep the model consistency.
General:
- REST and SOAP must be designed for Admin Panel integrations and be equal in terms of coverage. GraphQL should be designed for storefront scenarios.
- Any identifier exposed in guest APIs (for example, cart ID) must be masked to prevent the possibility of unauthorized access to the data of other guest users.
- Authentication must be done via
\Magento\Authorization\Model\UserContextInterface. - Customer-specific identifiers (such as customer ID or cart ID) must be deducted from the record of the successfully authenticated customer. They must not be accepted via request parameters.
- All new web API endpoints must be covered with web API functional tests.
- For REST and SOAP, by default, the same test will be executed in the scope of different continuous integration jobs. The base class for REST and SOAP tests is
\Magento\TestFramework\TestCase\WebapiAbstract - The base class for GraphQL tests is:
\Magento\TestFramework\TestCase\GraphQlAbstract
- For REST and SOAP, by default, the same test will be executed in the scope of different continuous integration jobs. The base class for REST and SOAP tests is
- Web API requests must be processed by custom front controllers with optimized routing to prevent the admin and storefront areas from executing routers.
- Web API schema should be strictly typed. (All complex types should eventually be resolved to scalar types.)
- Authentication parameters must be passed via headers.
- Throttling must be configured by the system integrator. It is not supported by Magento
- Internal server errors must be masked and never shown to the user in production mode. In developer mode, original exceptions must never be masked and should be displayed along with the related stacktrace.
- Pagination must be supported by all list operations.
GraphQL:
- Unlimited nesting should be supported during requests for related entities. (For example, get Order => Order Items => Products => Related Products)
- Field filtration must be performed with SQL queries. Do not filter on the application layer after you’ve fetched all possible fields.
- Third-party customizations must be done separately for Service Contracts and for GraphQL
- For modularity purposes, GraphQL configuration must be declared in a separate module. For example, to expose GraphQL for the module
MyModule, you must create theschema.graphqlsfile in theMyModuleGraphQlmodule. - GraphQL is primarily designed for store-front one-page apps and mobile applications. It supports token and cookie authentication, as well as guest access to public queries
- All queries must return the 200 HTTP status code. If an error occurs, return the error in the response body. A 500 status code is allowed when an exception occurs when generating a schema, but not during requests.
- The Store code should be passed via headers.
REST:
- The resource URL should be versioned (for example: V1). The version must be specified in the following format:
V\d.+ - Resource names in a URL should be in plural form (for example: products, carts)
- ID parameters for operations on entities should be part of the resource URL (for example: /V1/products/:sku )
- POST should be used to create an entity. PUT should be used to update an entity. PATCH should be used to patch (update only selected fields) an entity(s) update.
- REST is designed for system integrations, mobile app integrations, as well as for one-page apps. It supports tokens, cookies and OAuth 1.0 with token exchange. It also supports guest access to public resources.
- Responses must return responses with standard HTTP status codes.
- The store code must be passed via URL. For example
GET /rest/frenchStoreView/V1/products. Persistence operations that should be performed for all stores at once, should have ‘all’ store code in the URL.
SOAP:
- SOAP is designed for systems integration. It supports token authentication for customers and admins, as well as no authentication for anonymous service methods. Cookie authentication and OAuth 1.0 are not supported.
- The schema is available in the form of a WSDL for all exposed services.
- All requests must return the 200 HTTP status code. If an error occurs, return the error in the response.